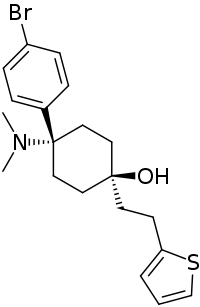
C-8813
C-8813 (thiobromadol) is a potent μ-opioid receptor agonist with a distinctive chemical structure which is not closely related to other established families of opioid drugs. The trans-isomer was found to be around 591 times more potent than morphine in animal studies.[1] The same study assigned a potency of 504 times that of morphine to the related compound BDPC.
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H26BrNOS |
| Molar mass | 408.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
C-8813 is claimed to be similarly potent at the δ-opioid receptor, which antagonizes the μ-induced depression of breathing, presumably making the drug safer.[1]
C-8813 has never been approved for use in humans.
References
- Liu ZH, Jin WQ, Dai QY, Chen XJ, Zhang HP, Chi ZQ (May 2003). "Opioid activity of C8813, a novel and potent opioid analgesic". Life Sciences. 73 (2): 233–41. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00263-7. PMID 12738037.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.