 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intramuscular injection, suppositories |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 8% (suppositories), 37% (oral solution) |
| Metabolism | mainly hepatic, at least 11 metabolites |
| Elimination half-life | 34 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
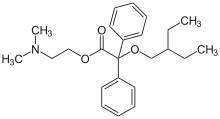
| Formula | C24H33NO3 |
| Molar mass | 383.532 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Denaverine is an antispasmodic drug. It was developed in Germany and patented in 1974. Denaverine hydrochloride is used in veterinary medicine under the trade name Sensiblex as a muscle relaxant for the myometrium of cows and dogs during parturition.[1] Under the trade name Spasmalgan, it has also been used in humans for the treatment of urogenital and gastrointestinal spasms.[2]
Mechanism of action
Denaverine, like papaverine, acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Additionally, it has anticholinergic effects.[3]
References
- ↑ Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products: Denavering Hydrochloride Summary Report
- ↑ Dootz H, Kuhlmann A, Hoffmann K, eds. (2005). Rote Liste (in German) (2005 ed.). Aulendorf: Editio Cantor. 77 023. ISBN 3-87193-306-6.
- ↑ Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (2010). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 4 (23 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.