 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Moctanin |
| Other names | 1-Mono-octanoin; glycerol monoctanoate; 1-monocaprylin; 1-monocapryloyl-rac-glycerol; 1-monooctanoin; 1-monooctanoylglycerol; caprylic acid α-monoglyceride; DL-1-monooctanoin; glyceryl 1-monooctanoate; octanoic acid 1-monoglyceride; α-monocaprylin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Injection through catheter into bile duct |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.112.381 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
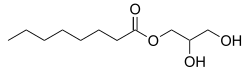
| Formula | C11H22O4 |
| Molar mass | 218.293 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Monoctanoin (or monocaprylin; trade name Moctanin) is a monoglyceride used to dissolve gallstones consisting of cholesterol. It is not available in the US any more.[1]
The drug was given by injection through a catheter into the bile duct. Its most common adverse effects were abdominal or stomach pain, usually mild, or a burning sensation.[1]
References
- 1 2 Monoctanoin (Injection) Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information. Accessed 28 April 2021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.