 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
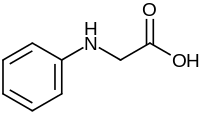
| IUPAC name
N-Phenylglycine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Anilinoacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.792 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 151.165 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 127–128 °C (261–262 °F; 400–401 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
N-Phenylglycine is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NHCH2CO2H. This white solid achieved fame as the industrial precursor to indigo dye.[1] It is a non-proteinogenic alpha amino acid related to sarcosine, but with an N-phenyl group in place of N-methyl.
Preparation
It is prepared by the Strecker reaction involving the reaction of formaldehyde, hydrogen cyanide, and aniline. The resulting amino nitrile is hydrolyzed to give the carboxylic acid.[2]

Pfleger's historic synthesis of indigo using N-phenylglycine
See also
- Phenylglycine, an isomer with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CO2H.
References
- ↑ Helmut Schmidt (1997). "Indigo – 100 Jahre industrielle Synthese". Chemie in unserer Zeit. 31 (3): 121–128. doi:10.1002/ciuz.19970310304.
- ↑ Elmar Steingruber "Indigo and Indigo Colorants" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2004, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_149.pub2
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.