Do Nothing
All things fall at 9.8m/s^2 and it takes a very significant increase in surface area for a shape shifter to be so affected by air resistance that you would get a slow fall effect. This is because your horse never "falls" more than a few inches per step. Since air resistance compounds exponentially with speed, your vertical air resistance would be next to nil.
Where you would see the most air resistance would be against the Coronal plane of the horse at full gallop.
The Air Drag equation is F = 0.6⋅c⋅A⋅v^2
F = Air Resistance
c = Drag Coefficent
A = Frontal Area
v = Air Velocity
To figure out how Ballon like your horse will be, I will solve for a border collie, a horse the weight of a border collie, and an 11" party balloon filled with air.
Since I can't find drag coefficients on dogs and horses, we'll have to look at humans instead. A human has an average c of 1.0-1.3. Horses have a slightly sleeker body design than a human; so, I will assume the low end of that at 1.0 and border collies have a lot of shaggy fur which creates more drag so I will assume they are at the high end at 1.3. Balloons are about a 0.5.
To find A I took a histogram of the front profile of an average sized horse, border collie, and balloon where each pixel is at the scale of 1/2".
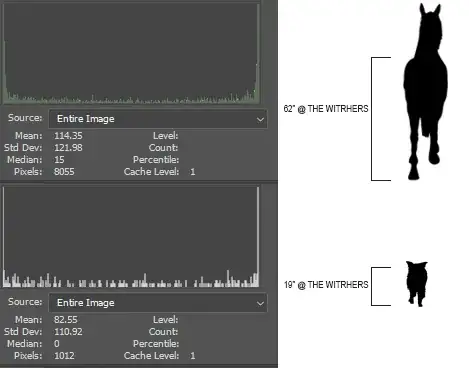

For the horse @ a Mean of 114.35 this silhouette is 55% black so if you take the 8055px each representing 1/2" by 1/2" your get a total Coronal plane surface area of 3612px = 903in^2 = 0.5826m^2.
For the dog @ a Mean of 82.55 this silhouette is 68% black so if you take the 1012px each representing 1/2" by 1/2" your get a total Coronal plane surface area of 684px = 171in^2 = 0.1103m^2.
For the ballon @ a Mean of 73.06 this silhouette is 71% black so if you take the 374px each representing 1/2" by 1/2" your get a total Coronal plane surface area of 266px = 66in^2 = 0.0426m^2.
v is just the top speed which for a horse is 12.5m/s and for the border collie 13.4m/s. For the ballon I will use the horses speed to simulate the air resistance at our target speed.
I will also use a mass of 17kg for the horse and dog, and 2g for the ballon filled with air.
So the force of friction from airdrag is:
So the air resistance of a horse is (0.6)(1)(0.5826)(156.25) = ~54.6N.
And for the border collie is (0.6)(1.3)(0.1103)(179.56) = ~15.4N.
And for the balloon is (0.6)(0.5)(0.0426)(156.25) = ~2.0N.
From this we can determine the coefficient of friction using μ = F/(M⋅v)
So the coefficient of friction of a horse is (54.6)/((17)(12.5)) = ~0.2569
And for the border collie is (15.4)/((17)(13.4)) = ~0.0676
And for the balloon is (2.0)/((0.002)(12.5)) = ~80.
This can then be plugged into a stopping distance equation d=v^2/(2μ)
So the stopping distance of the a horse is (156.25)/(2(0.2569)) = ~304m
And for the border collie is (179.56)/(2(0.0676)) = ~1333m
And for the balloon is ((156.25)/(2(80)) = ~0.98m.
What about Buoyancy
Going back to the average mass of a border collie at 17kg and comparing it to the average mass of a horse 380-1000kg, we see that the horse would have to be 22-59 times less dense than the dog, assuming that both animals have a density of about 1000 kg/m3, this gives a final density of somewhere in the range of 16-45 kg/m3. Since air has a density of 1.225kg/m3 the effective downward force of gravity - buoyancy would be somewhere between (17 - (1.225 / 16 * 17)) = 15.7kg and (17 - (1.225 / 45 * 17)) = 16.5kg.
This is not a significant enough reduction to cause a noticeable change, again, because the up and down motion of the horse is not very significant, one would no notice such a small change in downward acceleration unless they were extra-ordinarily observant and deeply familiar with horses.
Conclusion
As it turns out, density does not significantly affect how well an animal can move to nearly the degree we think it would. You can see that the horse experiences much more air resistance than the dog, but it's still so little that it would take 304m to come to a complete stop from air resistance alone. This is not at all like a balloon that would come to a stop in just under a meter at the same speeds. Since the horse makes ground contact about once per meter while at full gallop, this means it's total slowdown from air resistance between steps is still going to be too small to be perceivable, even if it is technically more than a dog or horse would normally experience.
As for comments about traction, the total difference in downward force between a dog and a horse sized dog from buoyancy is only 3-8%. However, the increased surface area of the hooves compared to the dog's paws is over 1000%. So, the horse sized dog would actually have WAY better traction as a horse than it did as a dog thanks to having so much more gripping surface to work with. This means the horse would not slip and slide at all like some answers have predicted. The bigger give-away would be its ability to stop too quickly; so, hopefully the shapeshifter has made it's hooves adequately slippery to properly emulate the right level of traction. But if the horse were to panic and have to stop of a dime, it could, which would give away that something is off about it.
The other real giveaways would be if a really observant person notices that the hooves aren't sinking into mud the way they should or if it runs into something it should be able to push through (like getting knocked over running into a small branch.)


